Blog
The Technical Examination for CSA Certification
This article aims to provide insight into the steps involved in the technical examination. This follows a fixed process that is always the same according to CSA criteria 2.8 to 2.21. and ensures that each applicant is analysed fairly and equally according to the standards. The basis for each technical examination for certification is three sample emails from customers/brands using the sender’s mailing platform, as well as the complete list of IP addresses and host names of the servers used to send the mailings.
IPs and email hosts
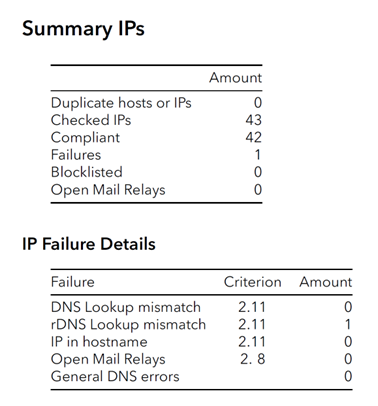
The IPs and host names provided by the sender form the basis of the first step of the technical check. This step checks whether the IPs and host names used meet the required criteria and is the starting point for the follow-up checks of the email samples and the reputation check monitoring. The IPs and host names also form the core of the certified IP list, which the CSA provides to the mailbox providers and other partners for daily retrieval. The check and analysis are automated and triggered by the CSA Tech team.
- First, the IPs and hosts are checked for duplicates. This is important to ensure that there are no duplicate entries that could cause confusion or errors later. An IP and its associated host are unique in combination and allowed once in the system.
- In the second step, the Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDN) are checked for suspicious syntax of dial-up networks. This checks whether the specified FQDNs follow generic procedures in naming dial-up networks. See also criterion 2.11 of the CSA criteria.
- Now, the DNS and reverse DNS check is carried out to ensure that the sending email servers can be uniquely identified.
If these initial checks are successful, the IPs and hosts are uploaded to the Certification Monitor for monitoring. After seven days of the first monitoring, the sender can access a test account to monitor its reputation.
Email conformity
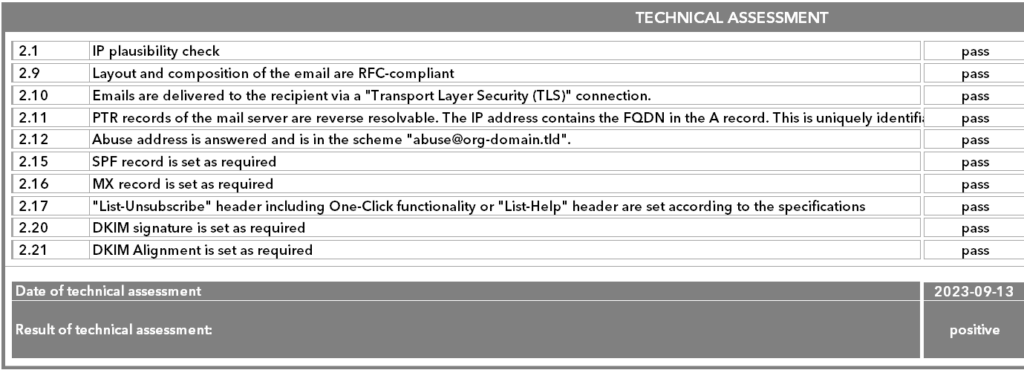
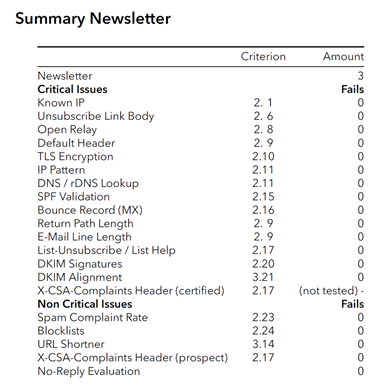
The next step is to check the three email samples for their conformity with the CSA criteria. This check is automated and is also triggered by the CSA Tech team.
- The email samples must have been sent from known IPs from the broad IP list. For this purpose, the received lines in the email header are analysed and compared with the IP list.
- The required authentication methods are then checked – SPF, DKIM and DKIM alignment are mandatory.
- This is followed by a check of the extended technical requirements, such as List Unsubscribe and the completeness of the DKIM signature.
The results of the automatic tests are documented and additionally viewed by the CSA Tech team and checked for plausibility. If there are any questionable test results, a manual review and check is carried out for confirmation or correction.
Documentation of the test results
Any deviations from the CSA criteria and all other test results are documented in an internal test report. Here, both the test points and the errors that occurred are recorded to ensure a complete record of the process. The first results of the reputation check are also recorded after at least seven days following the technical review. The technical results and the values of the first reputation check are then recorded in the check protocol. They are then transferred to the applicant by Client Success Management, together with the results of the legal part of the check.